If you’re learning C programming, understanding how to interchange two numbers is one of the first key concepts. It teaches you how variables work, how to use a temporary variable, and how logic flows in a program. This tutorial walks you through a simple C program to swap two numbers, its logic, and why it matters in programming basics.
What Does Interchanging Mean?
Interchanging (or swapping) two numbers means switching the values between two variables. For example:
Before:a = 10, b = 20
After interchanging:a = 20, b = 10
C Program to Interchange Two Numbers Using a Temporary Variable
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a, b, temp;
// Taking input from user
printf("Enter first number (a): ");
scanf("%d", &a);
printf("Enter second number (b): ");
scanf("%d", &b);
// Interchanging values using temp variable
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
// Displaying swapped values
printf("After interchanging:\n");
printf("a = %d\n", a);
printf("b = %d\n", b);
return 0;
}
Explanation of the Program
int a, b, temp;: Declares three integer variables.- User Input: Takes values for
aandbusingscanf. - Swapping Logic:
- Store value of
aintemp - Assign value of
btoa - Assign value of
temptob
- Store value of
- This ensures the values of
aandbare successfully interchanged.
Why Is Swapping Important?
- It’s a fundamental logic step in many algorithms like sorting.
- Helps build an understanding of variables, memory, and flow control.
- It’s often used in interview questions for beginners.
Other Ways to Interchange Numbers in C
You can also swap two numbers without using a temporary variable:
a = a + b; b = a - b; a = a - b;
However, this method is not always recommended due to potential integer overflow issues.
Related Topics You Might Like
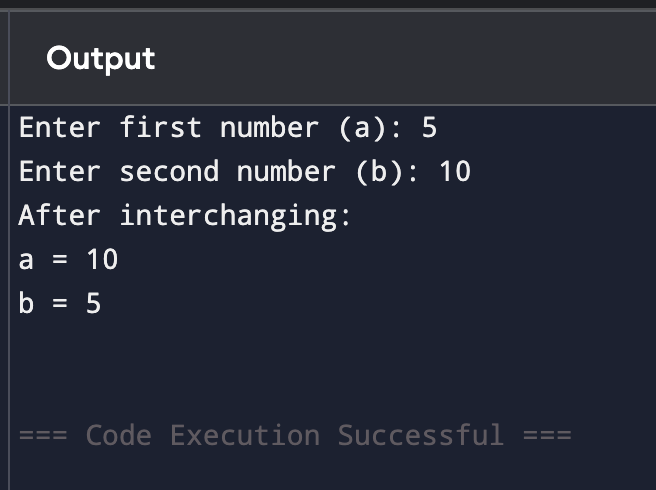
Output


[…] Difference Between Arrays and Loops in C […]